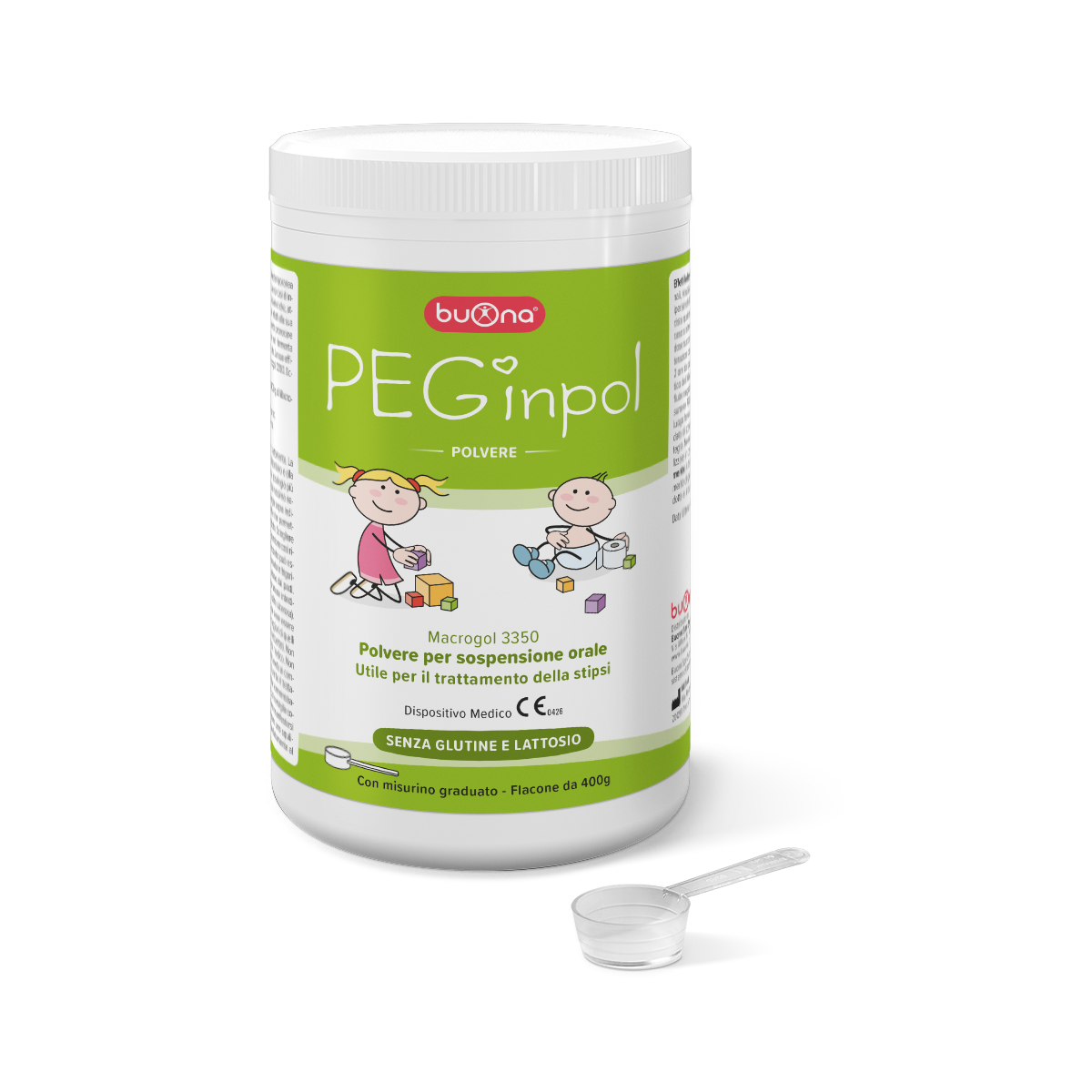
PEGinpol 100 g o 400 g
€14,80 – €23,80Price range: €14,80 through €23,80
Powder for oral suspension, useful for the treatment of constipation
Posologia
- Da 6 mesi a 2 anni (fino 12 Kg): 0,8 g/kg di peso corporeo al giorno
- Da 2 a 11 anni (da 12 Kg a 20 Kg): 1 g/kg di peso corporeo al giorno
- Al di sopra di 11 anni (+20 Kg):10-30g al giorno.
Peginpol è un dispositivo medico CE 0426. Leggere attentamente le avvertenze e le modalità d’uso.
AUT. MIN. DEL 19/12/2016
Buona Shipping | |
CONDIZIONI | COSTO |
Ordini inferiori a € 49,00 | € 6,00 |
Ordini superiori a € 49,00 | GRATIS |
Ordini superiori a € 29,00 | GRATIS |
Box Promozionali | GRATIS |
Acquisto di 1 confezione di Ugo e l'Olio | € 1,99 |
SPEDIZIONE GARANTITA: 3-5 GIORNI LAVORATIVI | |
PEGinpol is a product with a laxative effect that regulates the intestine by means of an osmotic mechanism (draws water into the intestine).
PEGinpol is recommended in cases of chronic constipation and occasional irregular bowel activity.
In fact, thanks to its affinity for water, PEGinpol causes a softening of the stool, facilitating evacuation without giving rise to emergency situations. Moreover, since the product is not absorbed, it does not ferment in the intestine or irritate the mucous membrane, and hence does not cause cramps or abdominal pain. It is eliminated in the feces in unmodified form.
ITS EFFECTIVENESS IS NOT DIMINISHED OVER TIME.
Read More ...
Stipsi funzionale e cronica
Prodotti consigliati
| Weight | N/A |
|---|---|
| Package |
a. Flacone da 100 g con misurino graduato ,b. Flacone da 400 g con misurino graduato |
Composition
One bottle contains: 100 g of Macrogol 3350.
PEGinpol IS GLUTEN AND LACTOSE FREE
How to use
- From 6 months to 2 years (up to 12 Kg): 0.8 g/kg body weight per day;
- From 2 years to 11 years (from 12 kg to 20 kg): 1 g/kg body weight per day;
- Over 11 years (or over 20 kg): 5 to 15 level measures per day.
More simply:
5-7 kg 2 level measures
7-9 kg 3 level measures
9-12 kg 4 level measures
12-15 kg 5 level measures
15-18 kg 6 level measures
18-20 kg 7 level measures
over 20 kg up to 15 level measures
The ideal daily dose for each age group should be determined according the child’s body weight, the severity of constipation and the individual’s response to treatment.
Do not administer the product to young children unless advised to do so by a doctor.
The maximum necessary dose does not normally exceed 30 g of product per day.
With reference to the dosages indicated above, measure out the appropriate quantity of the product using the graduated measuring cap, where the first mark corresponds to 0.5 g, the second mark to 1 g and a level measure to 2 g.
Dissolve level measure of the product (2 g) in quarter full glass of water (about 25 ml). Drink the resulting solution.
The daily dose maybe divided into multiple administrations
The product may be prepared in advance in the appropriate volume of water and stored in a fridge, in a covered container, for up to 24 hours.
PEGinpol should be assumed between meals.
WARNINGS
Do not exceed the recommended dose, as higher doses can
cause unexpected side effects.
While taking PEGinpol is advisable to follow an appropriate diet and assume an oral rehydration solution (ORS) in order to prevent dehydration; it is advisable to consult your doctor irrespective of the result of the treatment.
Do use the product for more than 30 consecutive days; if symptoms persist
seek medical advice.
Do not use in the event of intolerance to the product and hypersensitivity to components and to
Polyethylene glycol (PEG).
Do not administer to children under 6 months.
Do not use in case of intestinal obstruction.
Do not take PEGinpol in the event of: intestinal stenosis, intestinal perforation,
inflammatory bowel diseases (such as Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis).
Information
Chronic idiopathic constipation is a common gastrointestinal disorder in infants and children during the first months and years of life. Must be diagnosed by a doctor.
There are two possible approaches for the treatment of chronic idiopathic constipation in children:
– Non pharmacological: Normal introduction of fiber and fluids into the diet, regular physical activity
and possible use of probiotics and prebiotics.
– Pharmacological: Divided into two key stages, i.e. fecal disimpaction
(eliminating feces in the gut), only when necessary, and subsequent maintenance
therapy.
PEG3350 (PEGinpol) represents a viable solution in the case of pharmacological treatment, since it is not absorbed in into the intestine, and is not metabolized by intestinal bacteria, hence it does not cause cramps or abdominal pain.
it works by drawing water into the lumen of the colon, leading to rehydration and softening of the stool, and a mechanical stimulation of intestinal peristalsis.